Implementing SOC 2 common criteria in Qatar ensures data security by establishing strong controls, continuously monitoring systems, and managing risks effectively.
The SOC 2 Common Criteria is a globally recognised framework by the AICPA that helps organisations maintain strong internal controls and ensuring secure, efficient operations through areas like access controls, risk assessment, and monitoring. This framework is increasingly critical for Qatari businesses facing sophisticated cyber threats.
The threat landscape in Qatar demonstrates this urgency. In 2022, Qatar blocked about 23 million cybersecurity threats. This included more than 4 million malicious emails and nearly 8 million malware attacks.
Given these challenges, Qualitas Consulting helps Qatari businesses implement SOC 2 compliance efficiently, offering expert guidance tailored to the region’s unique regulatory and threat environment.
What are the Common Criteria for SOC 2?
The SOC 2 framework uses Common Criteria (CC1-CC9) to evaluate an organization’s security controls and operational safeguards. These nine criteria form the mandatory Security category of the Trust Services Criteria and establish how companies protect sensitive data, manage risks, and ensure reliable operations.
The nine Common Criteria include:
- CC1: Control Environment
- CC2: Communication and Information
- CC3: Risk Assessment
- CC4: Monitoring Controls
- CC5: Control Activities
- CC6: Logical and Physical Access Controls
- CC7: System Operations
- CC8: Change Management
- CC9: Risk Mitigation
Note: These criteria are explained in detail in the sections below.
For Qatari companies, using these criteria meets global standards. It also boosts cybersecurity governance in line with local laws, such as the National Cyber Security Strategy and Data Privacy Law No. 13 of 2016.
In fact, Qatar was ranked a “Tier 1 Model” country in the Global Cybersecurity Index 2024. It achieved top scores across all five cybersecurity pillars.
The Five SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria (TSC) Explained
SOC 2 compliance is evaluated against five Trust Services Criteria (TSC) developed by the AICPA (American Institute of CPAs). Each TSC addresses a specific aspect of secure and reliable operations. Security is mandatory for all organizations, while the other four are optional. It should be selected based on your business operations and customer commitments.
| TSC | Status | Purpose & Focus | Key Control Areas | When to Include | Qatar Industry Examples |
| Security(Common Criteria) | Mandatory | Protects systems and data from unauthorized access, breaches, and vulnerabilities | – CC1-CC9 controls – Access controls – Encryption – Authentication – Risk assessment – Monitoring | Required for ALL SOC 2 audits | – Qatar Central Bank-regulated fintech platforms implementing multi-factor authentication – Cloud providers serving government entities with NCSA-compliant access controls |
| Availability | Optional | Ensures systems remain operational and accessible during agreed-upon timeframes | – Uptime guarantees – Disaster recovery – Business continuity – System monitoring – Redundancy | Include if you have SLAs or uptime commitments to customers | – Banks maintaining 99.9% uptime per Qatar Financial Centre requirements – E-government platforms ensuring 24/7 accessibility for citizens |
| Processing Integrity | Optional | Guarantees data processing is complete, accurate, valid, timely, and authorized | – Transaction accuracy – Data validation – Error detection – Quality assurance – Authorization workflows | Include if you process transactions, payments, or critical data transformations | – SaaS platforms processing Qatar Stock Exchange data – Healthcare systems ensuring accurate patient record processing under MOH regulations |
| Confidentiality | Optional | Protects sensitive information designated as confidential from unauthorized disclosure | – Data classification – Encryption standards – NDAs enforcement – Access restrictions – Secure transmission | Include if you handle proprietary business data, trade secrets, or competitive information | – Healthcare providers encrypting patient data per Data Privacy Law No. 13 of 2016 – Energy sector companies protecting infrastructure blueprints |
| Privacy | Optional | Demonstrates ethical handling of personal information in compliance with privacy regulations | – Consent management – Data minimization – Individual rights – Cross-border transfers – GDPR/privacy law compliance | Include if you collect, store, or process personal data, especially EU citizens’ data | – Telecom providers (Ooredoo, Vodafone Qatar) adhering to GDPR for EU customers – E-commerce platforms managing Qatar resident data under local privacy laws |
These criteria help organisations build a strong security structure. This supports regulatory alignment, boosts operational efficiency, and fosters customer trust.
The diagram below illustrates how these components relate to each other:
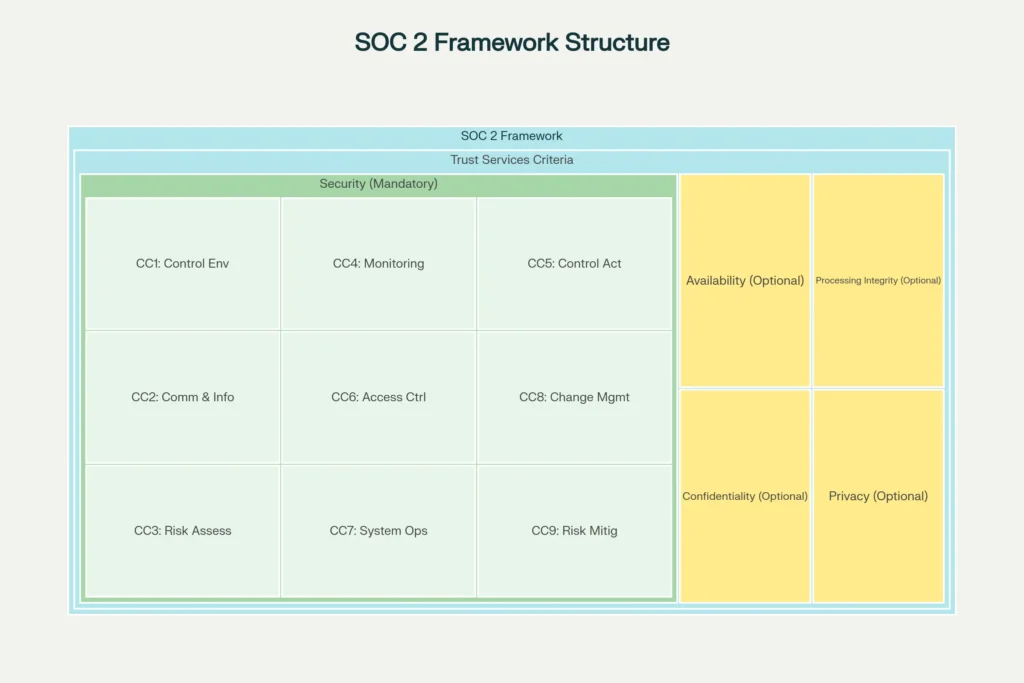
Understanding the SOC 2 Security Framework in Qatar: Common Criteria (CC1-CC9)
The SOC 2 compliance framework is built on two foundational layers: Trust Services Criteria and Common Criteria. Understanding this structure helps organisations establish robust security controls and demonstrate compliance to stakeholders.
Security Category (Mandatory)
The Security category forms the mandatory foundation of every SOC 2 audit. It contains nine Common Criteria (CC1-CC9) that establish operational and administrative safeguards. These criteria protect systems and data from unauthorized access and threats.
- CC1: Control Environment sets the organizational tone for accountability and security. It establishes roles, responsibilities, and ethical governance frameworks that guide security decisions across the organization.
- CC2: Communication and Information ensures critical security information flows accurately across all organizational levels. This enables consistent implementation of controls and policies.
- CC3: Risk Assessment defines processes for identifying potential security risks, threats, and vulnerabilities. It establishes frameworks for evaluating their impact and likelihood.
- CC4: Monitoring Controls implements continuous oversight mechanisms. These track system performance, detect anomalies, and measure control effectiveness.
- CC5: Control Activities enforces specific security processes and procedures. These mitigate identified risks and prevent unauthorized activities within critical systems.
- CC6: Logical and Physical Access Controls manages user authentication and permissions. This ensures only authorized personnel can access sensitive resources.
- CC7: System Operations maintains system stability, performance, and uptime. Proactive monitoring and maintenance procedures ensure business continuity. The Qatar National Cyber Security Agency (NCSA) reported in its 2024–2030 strategy that continuous system monitoring of critical infrastructure is now a national objective.
- CC8: Change Management controls all modifications to IT systems and infrastructure. Formal approval processes prevent unintended disruptions and security vulnerabilities. In March 2024, a major data breach revealed flaws in change control at a social platform in Qatar. This led to enforcement action by the NCSA.
- CC9: Risk Mitigation applies corrective and preventive actions. These address identified risks, incidents, and control failures to enhance organizational resilience. From March 2022 to February 2023, more than 2,000 dark-web leak posts involved GCC organisations, including Qatar. This shows a clear need for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Optional Trust Services Categories
Beyond mandatory Security controls, organizations can implement additional Trust Services Criteria. These address specific business needs and industry requirements.
- Availability ensures systems remain operational during agreed-upon service windows. It demonstrates commitment to business continuity and disaster recovery planning.
- Processing Integrity guarantees all data processing is complete, accurate, and authorized. This prevents errors and unauthorized modifications that could compromise data quality.
- Confidentiality protects sensitive business and customer information from unauthorized disclosure. Organizations implement encryption, access controls, and classification frameworks.
- Privacy demonstrates compliance with personal data protection regulations. It implements procedures for transparent data collection, secure handling, and consent management.
Relationship Between Layers
The mandatory Security criteria (CC1-CC9) provide foundational infrastructure. This supports all other optional Trust Services Categories. Organizations implementing additional criteria build upon this foundation. This creates a comprehensive security and compliance posture addressing both general operational security and industry-specific requirements.
SOC 2 Framework Mapping with ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR
Mapping SOC 2 with other standards improves efficiency and compliance effectiveness.
| Framework | Overlap with SOC 2 | Benefits for Qatari Businesses |
| ISO 27001 ISMS | Information security, risk treatment, business continuity planning | Simplifies global client audits and strengthens internal controls |
| NIST CSF | Risk identification, incident response process | Improves IT infrastructure security for critical sectors |
| GDPR | Privacy, consent, and personal data handling | Ensures Qatari companies processing EU data meet international requirements |
Ensures that Qatari companies processing EU data meet international requirements.
Cross-mapping reduces redundant work. It brings together the control environment and helps Qatari companies meet local and international expectations effectively.
Explore our services to integrate ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR compliance into your business.
Key Benefits of SOC 2 Compliance for Organisations in Qatar
Implementing SOC 2 provides tangible advantages:
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Demonstrates robust data protection compliance and secure operations.
- Operational Efficiency: Unified controls reduce duplication and improve process monitoring.
- Vendor Assurance: Strengthens vendor risk management by showcasing secure practices.
- Regulatory Alignment: Simplifies adherence to local cybersecurity policies and cloud security compliance standards.
- Preparedness for Disruption: Incorporates business continuity management and a solid incident response process.
For businesses in Qatar, these benefits offer a competitive edge and boost credibility in both regional and global markets. Qatar’s cybersecurity market is projected to hit US$143 million by 2025. In 2022, 18% of businesses reported breaches. This shows the growing importance of compliance and vendor assurance.
Real-World Business Applications
SOC 2 compliance is practical and industry-specific:
- SaaS Providers: Meet SaaS compliance requirements and assure clients of secure cloud operations.
- Financial Institutions: Use control activities to prevent fraud and ensure transaction integrity.
- Healthcare providers: Apply data protection compliance and access control policies for patient confidentiality.
- IT & Telecom Companies: Track operations using system monitoring for threat detection and response.
A Doha-based cloud provider can expand services to European and U.S. clients. They can do this by demonstrating compliance and operational reliability through a SOC 2 readiness assessment.
Common Implementation Challenges
Achieving SOC 2 certification presents challenges:
- Documentation Gaps: Missing information security policy or inadequate evidence of controls.
- Overlapping Frameworks: It’s hard to combine SOC 2 with ISO 27001 mapping and GDPR.
- Continuous Monitoring: Resource-intensive monitoring controls without automation.
- Incident Management: An inefficient incident response process may delay mitigation.
- Change Management: Weak change management procedures can compromise system integrity.
Addressing these challenges requires leadership support, automation tools, and ongoing staff training.
Steps to Achieve SOC 2 Compliance in Qatar
A clear roadmap helps businesses achieve SOC 2 readiness:
- Conduct a SOC 2 readiness assessment to identify gaps.
- Define the audit scope and applicable systems.
- Develop policies such as the information security policy and access control policies.
- Implement controls, including CC1–CC9 criteria.
- Conduct internal audits and stress tests.
- Engage external auditors to generate the SOC 2 audit report.
- Maintain compliance using compliance automation software and continuous system operation and monitoring.
Using this method makes getting certified easier and helps maintain compliance over time.
We offer hands-on SOC 2 support. This includes readiness assessments and full implementation, along with our pre-assessment audit services.
Expert Support for Your Compliance Journey in Qatar
Working with experts ensures efficient SOC 2 adoption. QualitasQA helps Qatari businesses:
- Conduct a SOC 2 readiness assessment and gap analysis.
- Map SOC 2 controls to ISO 27001 ISMS and GDPR.
- Implement compliance automation tools for ongoing monitoring.
- Prepare and review documentation for a successful SOC 2 audit report.
This guidance helps organisations improve cybersecurity governance. It reduces audit fatigue and allows them to confidently expand services worldwide.
We help Qatari businesses achieve SOC 2 compliance with our certification audit support services.
Conclusion
The SOC 2 Common Criteria helps organisations in Qatar. It keeps systems secure, makes operations reliable, and ensures processes are compliant. Businesses can manage risks and protect data by having a strong control environment.
SOC 2 compliance boosts cybersecurity governance. It aligns with ISO 27001 and GDPR. This also supports business continuity management. As a result, organisations can respond better to threats.
Adopting the SOC 2 Common Criteria in Qatarchanges data protection from just a compliance task to a key strategy. This shift helps businesses grow sustainably and build trusted relationships.
We are committed to securing your organisation and building trust through SOC 2 compliance. Contact us today via our contact page to discuss how our expertise can support your business.
FAQS
1. What are the common criteria for SOC 2?
The Common Criteria in SOC 2 include nine key control areas (CC1–CC9). The AICPA set these to assess an organisation’s governance, risk management, access controls, and operational safeguards. These controls are essential for protecting data and systems
2. What are the criteria for SOC 2 certification?
SOC 2 certification relies on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC). These criteria assess how well a company protects customer data. They cover five key areas: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy.
3. What are the five principles of SOC 2?
The five SOC 2 principles are Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. They serve as the foundation for evaluating a service organisation’s controls.
4. What is the SOC 2 compliance checklist?
A SOC 2 compliance checklist has several key steps:
Define the scope.
Implement security controls.
Conduct risk assessments.
Monitor systems.
Document policies.
Perform internal audits.
Engage an independent auditor for attestation.



