Global partnerships demand proof of trustworthiness. Modern enterprises face mounting pressure to demonstrate security capabilities.
Research shows nearly two-thirds of organizations report that potential buyers, investors, and partners now require SOC 2 compliance verification before signing contracts. This attestation has become the golden standard across B2B SaaS industries.
Qatar businesses expanding into international markets encounter this reality daily. Contracts slip away when compliance credentials are absent. Audit failures create reputational damage that takes years to repair. The consequences extend beyond lost revenue—they impact market positioning entirely.
A structured SOC 2 audit checklist transforms this challenge into an opportunity. Breaking down complex requirements into manageable milestones makes certification achievable. Qatar’s growing technology sector positions local businesses perfectly for compliance success.
This comprehensive guide delivers actionable steps specifically designed for Qatari enterprises.
What is SOC 2 Compliance?
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants developed the SOC 2 compliance framework. Service organizations handling customer data require this specialized audit standard. It evaluates how companies safeguard client information through operational controls.
Two distinct audit types exist within the framework.
- SOC 2 Type 1 examines whether controls are properly designed.
- SOC 2 Type 2 goes further by testing operational effectiveness. Type 2 requires a minimum six-month observation period. Most clients and partners prefer Type 2 because it demonstrates sustained commitment.
Qatar businesses pursuing global expansion find SOC 2 increasingly non-negotiable. Cloud hosting providers, SaaS platforms, data centers, and IT service companies face the highest demand. Industry data confirms that this compliance framework consistently ranks among the top three most critical certifications. All revenue categories and industry sectors recognize their importance equally.
The framework aligns naturally with Qatar National Vision 2030’s digital transformation goals. Building data security frameworks strengthens the nation’s technological infrastructure. Companies certified in SOC 2 gain competitive advantages in regional markets. Partners view certification as evidence of operational maturity and reliability.
Read more: What Does SOC 2 Stand For and Why It Matters for Businesses in Qatar?
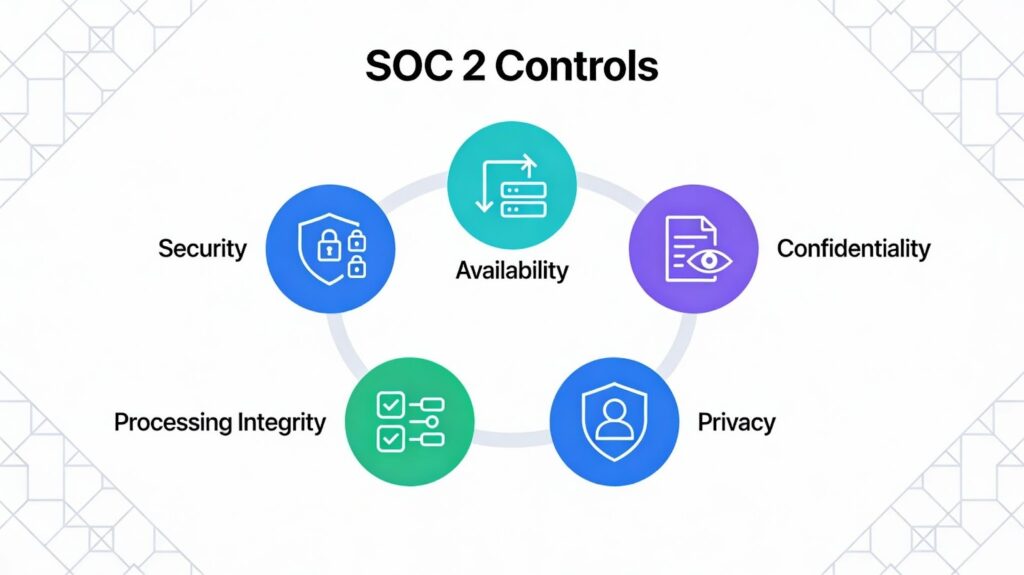
The Five Trust Services Criteria (TSC)
Understanding the foundation helps navigate the SOC 2 audit process successfully. Five distinct criteria form the framework’s backbone.
- Security serves as the mandatory baseline criterion for all audits. It addresses protection against unauthorized access to systems and data. Network controls, access management, and threat detection fall within this category. Every organization pursuing SOC 2 must demonstrate robust security measures.
- Availability focuses on system accessibility and uptime commitments. Service level agreements require documented evidence of performance monitoring. Business continuity planning and disaster recovery capabilities prove operational resilience. Qatar businesses serving international clients find this criterion particularly relevant.
- Confidentiality protects information designated as confidential through agreements or policies. Encryption, access restrictions, and non-disclosure agreements support this criterion. Organizations handling proprietary client data prioritize confidentiality alongside security.
- Processing Integrity ensures systems process data completely, accurately, and timely. Transaction validation, error detection, and quality assurance procedures demonstrate compliance. Financial platforms and payment processors emphasize the Trust Service Criteria heavily.
- Privacy governs personal information collection, usage, retention, and disclosure practices. Qatar’s Personal Data Privacy Law creates natural alignment opportunities here. Privacy policies, consent mechanisms, and data subject rights require thorough documentation.
Organizations at higher maturity levels within cybersecurity frameworks show overwhelming adoption rates. Studies reveal that91% of repeatable-tier organizations and 96% of risk-informed tier companies pursue SOC 2 requirements. This demonstrates the framework’s credibility across sophisticated security programs.
Complete SOC 2 Audit Checklist: 8-Step Process for Qatar Businesses
Breaking down the journey into actionable stages removes complexity entirely. Each phase builds upon previous accomplishments systematically.
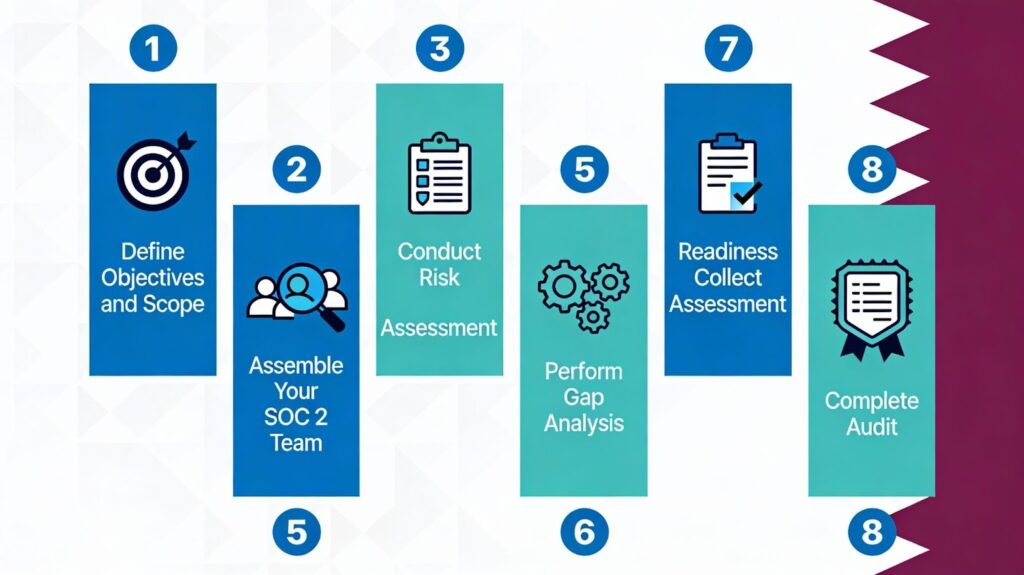
Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
Begin by identifying which Trust Service Criteria apply to your operations. Security remains mandatory, but other criteria depend on customer requirements. Some clients demand all five criteria while others need only two.
Determine whether Type 1 or Type 2 better serves your objectives. Type 1 provides faster initial certification but offers limited market value. Type 2 requires longer commitment but delivers substantially greater credibility.
Define system boundaries precisely to avoid audit scope confusion later. Include all infrastructure, applications, and processes handling customer data. Document third-party services and cloud platforms within your environment carefully.
Consider Qatar-specific regulatory requirements like MISA guidelines or QCB frameworks. Alignment opportunities reduce duplicate compliance efforts significantly. Establish realistic timelines accounting for resource availability and observation periods.
Step 2: Assemble Your SOC 2 Team
Cross-functional collaboration drives certification success more than any other factor. Appoint a dedicated project manager with executive sponsorship backing them. This individual coordinates activities across all departments and tracks progress.
Include IT security leads, compliance officers, and operations managers early. HR representatives handle personnel security controls and background check documentation. Finance teams manage vendor contracts and service level agreement tracking.
Decide whether external consultants bring the necessary expertise your team lacks. Qatar’s growing compliance market offers local and international advisory options. Internal resources understand company culture but may lack specialized audit knowledge.
Create a responsibility assignment matrix clarifying who owns each control area. Training requirements vary based on personnel experience with SOC 2 implementation projects. Schedule regular team meetings to address blockers and maintain momentum.
Step 3: Conduct Risk Assessment
Identify threats targeting each applicable Trust Service Criteria systematically. Cyber threats, operational failures, and insider risks require thorough evaluation. Qatar businesses face region-specific considerations like geopolitical factors and infrastructure dependencies.
Build comprehensive asset inventories covering hardware, software, and data repositories. Cloud subscriptions, on-premise systems, and mobile devices all require documentation. Knowing what you own enables proper protection strategies.
Vulnerability assessments reveal weaknesses before attackers or auditors discover them. Third-party vendor relationships introduce inherited risks requiring ongoing monitoring. Document findings in a risk register with severity ratings attached.
Organizations already holding ISO 27001 certification can leverage existing risk assessments. Mapping between frameworks reduces duplicated effort while strengthening both programs. This integration approach accelerates the timeline dramatically for prepared organizations.
Step 4: Perform Gap Analysis
Compare your current security posture against SOC 2 requirements comprehensively. Identify where existing controls fall short of audit standards. Honest assessment prevents surprises during official examinations later.
Prioritize control deficiencies based on implementation difficulty and audit impact. Some gaps require significant technology investments, while others need policy updates. Resource allocation decisions depend on accurate gap severity understanding.
Create detailed remediation roadmaps with realistic timelines for each deficiency. Assign owners to specific gaps, ensuring accountability remains clear. Track progress weekly to maintain forward momentum toward readiness.
Industry research reveals that insufficient monitoring evidence causes 68% of audit failures. Organizations often implement controls properly but fail to document their operation. Evidence collection planning must begin during gap analysis, not afterward.
Gap closure forms the bulk of pre-audit work requiring systematic attention. Don’t know where to start? Our Pre-Assessment Audit identifies every control gap holding you back.
Step 5: Implement and Remediate Controls
Design controls specifically addressing identified gaps from previous analysis. Technical controls include encryption, multi-factor authentication, and centralized logging systems. Administrative controls encompass policies, procedures, and training programs.
Physical controls matter for Qatar businesses maintaining local data centers. Access badges, surveillance systems, and visitor logs provide necessary protections. Cloud-first organizations need fewer physical controls but must verify provider compliance.
Test each control’s effectiveness before considering it operational and complete. Automated testing tools accelerate validation while ensuring consistency across environments. Manual testing remains necessary for administrative and physical control categories.
Document implementation thoroughly, including configuration screenshots and approval records. Auditors require evidence that controls operated as designed throughout observation periods. Change management processes ensure modifications don’t inadvertently weaken existing protections.
Step 6: Collect and Organize Evidence
Audit evidence determines whether certification succeeds or fails completely. Multiple evidence types support different control categories across the framework. Screenshots, system logs, policy documents, and meeting minutes all serve purposes.
Automated collection tools dramatically reduce manual burden while improving consistency. Security information and event management platforms aggregate logs from distributed systems. Compliance automation software maps evidence directly to specific SOC 2 compliance checklist requirements.
Establish clear naming conventions and logical folder structures from day one. Type 2 audits covering twelve months generate enormous evidence volumes. The organization prevents last-minute scrambles when auditors request specific documentation.
Map each piece of evidence to particular controls and criteria requirements. Gaps become visible quickly when systematic tracking exists. Retention requirements demand maintaining evidence throughout observation periods, plus audit duration.
Step 7: Conduct Readiness Assessment
Internal mock audits identify remaining weaknesses before official examinations begin. Simulate the actual audit experience by reviewing evidence and interviewing personnel. This rehearsal builds confidence while revealing overlooked deficiencies.
Test staff understanding through mock auditor interviews across all departments. Employees should articulate how they execute controls without reading scripts. Genuine comprehension matters more than memorized responses during actual audits.
Validate evidence completeness by sampling controls across each applicable criterion. Missing documentation discovered now can still be remediated without consequences. Issues found during official audits result in findings that weaken reports.
Current trends show 58% of organizations now conduct four or more audits annually. Enterprises average more than six different compliance examinations each year. This audit fatigue makes readiness assessments increasingly valuable for streamlining efforts.
Address final remediation needs emerging from readiness reviews promptly. Policy updates, control refinements, and documentation improvements strengthen overall posture. The investment in pre-audit preparation pays dividends through cleaner reports.
Step 8: Engage Auditor and Complete SOC 2 Audit
Selecting qualified auditors requires careful evaluation of credentials and industry experience. Verify firms hold appropriate AICPA licenses for conducting SOC 2 examinations. Big Four accounting firms bring prestige but command premium fees. Boutique firms often provide personalized attention and specialized expertise in specific industries.
Consider these critical factors during auditor selection:
- Request detailed proposals covering scope, timeline, fees, and team backgrounds
- Verify previous experience with similar organizations in your industry
- Check references from clients who completed recent SOC 2 audits
- Evaluate communication style and responsiveness during initial interactions
- Confirm understanding of Qatar’s regulatory landscape and business environment
Reports show that organizations that adequately prepare for SOC 2 audits achieve a 40% higher success rate on their first attempt.
Kick-off meetings establish clear expectations and communication protocols for fieldwork. Respond promptly to auditor requests throughout the certification process. Professional, organized responses demonstrate control environment maturity effectively. Report issuance typically occurs two to four weeks after completion.
Get professional guidance for your SOC 2 audit. Visit our Certification Audit Support Services.
Common SOC 2 Controls Checklist for Qatari Businesses
Specific controls form the backbone of compliance success across all criteria. This practical checklist guides implementation planning effectively.
Security Controls (Common Criteria)
Every organization requires these foundational security measures regardless of the optional criteria.
☐ Multi-factor authentication is enforced for all system access points consistently
☐ Password policies meeting complexity, length, and rotation requirements documented
☐ Role-based access control limiting permissions to job function necessities
☐ Network segmentation, separating production environments from development and testing
☐ Firewall rules documented, reviewed quarterly, and restricted to necessary traffic
☐ Intrusion detection and prevention systems monitor network activity continuously
☐ Encryption protects data at rest and during transmission, always
☐ Vulnerability scanning performed monthly with critical findings remediated immediately
☐ Patch management processes ensuring timely security update deployment
☐ Incident response plans documented, tested annually, and communicated broadly
☐ Security awareness training completed by all personnel annually, at a minimum
☐ Background checks are conducted for employees accessing sensitive systems routinely
Availability Controls
System uptime and performance commitments require these business continuity protections.
☐ Business continuity plans documented with recovery time objectives specified
☐ Disaster recovery procedures tested annually with results documented thoroughly
☐ System monitoring and alerting configured for performance and availability metrics
☐ Capacity planning is conducted quarterly to prevent resource exhaustion issues
☐ Backup procedures automated and verified through regular restoration testing
☐ Redundancy implemented for critical systems, eliminating single points of failure
☐ Service level agreements defined with customers and tracked against actuals
☐ Change management processes preventing unauthorized or untested production modifications
Confidentiality Controls
Protecting designated confidential information requires these specialized data protection measures.
☐ Data classification policies defining confidentiality levels and handling requirements
☐ Non-disclosure agreements signed by employees, contractors, and vendors annually
☐ Confidential data inventory maintained with storage locations and access documented
☐ Secure data disposal procedures ensuring complete destruction when retention expires
☐ Access restrictions limiting confidential information to authorized personnel only
☐ Encryption is enforced for all confidential data transmission internally and externally
Processing Integrity Controls
Transaction accuracy and completeness depend on these data accuracy safeguards.
☐ Data validation rules configured, preventing invalid or incomplete input
☐ Error detection and correction procedures documenting investigation and resolution
☐ Transaction logging capturing sufficient detail for reconstruction and reconciliation
☐ Quality assurance testing performed before production deployment of code changes
☐ Reconciliation procedures comparing system outputs against expected results regularly
☐ Processing completeness checks, ensuring all transactions complete successfully automatically
Privacy Controls
Personal information handling requires these privacy compliance implementations aligned with Qatar PDPL.
☐ Privacy policies published, accessible, and written in clear language
☐ Consent mechanisms capturing explicit permission before personal data collection
☐ Data subject rights procedures supporting access, correction, and deletion requests
☐ Third-party data sharing agreements reviewed annually for compliance alignment
☐ Privacy impact assessments conducted when introducing new processing activities
☐ Data retention and disposal schedules documented and enforced systematically
☐ Privacy training provided to all staff handling personal information regularly
Read more: What is the SOC 2 Common Criteria in Qatar and How Does It Ensure Data Security?
SOC 2 Documentation Requirements
Proper documentation transforms controls from concepts into verifiable proof that auditors accept. Comprehensive compliance documentation separates successful certifications from failed attempts.
- System descriptions form the foundation by explaining architecture, boundaries, and components. Network diagrams, data flow maps, and infrastructure inventories provide the necessary context. Cloud platform documentation includes service provider SOC 2 reports ideally.
- Policies establish management’s commitment to security and operational excellence clearly. Information security, access control, change management, and incident response policies remain mandatory. Review and approval workflows with version control demonstrate governance maturity.
- Procedures translate high-level policies into step-by-step operational instructions that staff follow. Testing procedures, backup procedures, and user provisioning procedures guide consistent execution. Screenshots and configuration examples enhance clarity significantly for technical procedures.
- Risk assessments require annual updates at a minimum, with interim reviews for significant changes. Document identified risks, likelihood ratings, impact assessments, and mitigation strategies. Executive review and acceptance of residual risks demonstrates informed decision-making.
- Vendor management documentation proves third-party oversight throughout contractual relationships. Due diligence assessments, SOC 2 report reviews, and ongoing monitoring evidence remain critical. Service level agreements and data processing agreements require annual review cycles.
- Monitoring evidence includes system logs, security alerts, scanning results, and analytics dashboards. Automated collection ensures completeness while reducing manual effort substantially. Log retention policies must align with observation period requirements.
- Testing records demonstrate control effectiveness through penetration tests, disaster recovery drills, and security assessments. Independent testing provides stronger evidence than self-assessments in auditor evaluation. Schedule major testing activities during observation periods for maximum audit value.
- Management review documentation shows executive oversight through security committee meetings and quarterly reviews. Meeting minutes, action item tracking, and decision documentation prove active governance. Leadership involvement signals organizational commitment, which auditors value highly.
Typical Timeline for SOC 2 Compliance
Initial preparation phases consume three to six months for most organizations. Gap analysis, risk assessment, and control implementation require substantial effort. Organizations with immature security programs need longer preparation periods, realistically.
- SOC 2 Type 1 audits typically involve two to four weeks of fieldwork. Auditors examine control design at a specific point in time. Report issuance follows within two to four weeks after fieldwork concludes.
- SOC 2 Type 2 requires a minimum of six months of observation periods before auditing begins. Twelve-month periods provide stronger evidence and greater market credibility. Organizations can’t accelerate observation periods regardless of resource investment.
Type 2 fieldwork extends four to eight weeks, depending on complexity. Larger environments with multiple locations require extended examination periods. Auditor availability during busy seasons also impacts scheduling significantly.
Report issuance takes two to four weeks following fieldwork completion. Management responses to findings and quality reviews cause this delay. Rush requests rarely succeed, given the careful review process required.
Studies show that organizations at advanced maturity stages demonstrate overwhelming adoption patterns. More than nine out of ten companies at repeatable and risk-informed tiers pursue SOC 2 compliance. This correlation suggests that mature security programs find certification more achievable.
Common SOC 2 Challenges in Qatar and How to Overcome Them
Anticipating obstacles allows proactive solutions rather than reactive firefighting approaches.

- Challenge: Limited local SOC 2 expertise creates knowledge gaps, slowing progress.
Solution involves partnering with experienced international consultancies offering virtual services. Online training resources and certification programs build internal capabilities over time. Regional expertise grows as more Qatari organizations successfully implement SOC 2.
- Challenge: Balancing local regulations with SOC 2 confuses priorities.
Solution requires mapping Qatar PDPL and MISA requirements to Trust Service Criteria. Integrated compliance approaches efficiently satisfy both frameworks. Legal counsel specializing in data privacy provides valuable guidance here.
- Challenge: Resource constraints in SMEs limit staff availability for compliance initiatives.
Solution involves phased approaches, prioritizing security criteria before optional ones. Automation tools maximize limited team productivity significantly. External consultants supplement internal capacity during peak demand periods cost-effectively.
- Challenge: Vendor management complexity overwhelms organizations with extensive third-party dependencies.
Solution includes standardizing vendor assessment questionnaires and reducing evaluation inconsistencies. Centralized oversight through vendor management platforms improves visibility and tracking. Risk-based approaches focus resources on the highest-risk vendor relationships appropriately.
- Challenge: Cultural resistance to documentation hinders evidence collection efforts substantially.
Solution demonstrates business value through contract wins and competitive advantages gained. Celebrate compliance milestones, maintaining team motivation throughout lengthy processes. Recognition programs reward individuals who contribute exceptional effort toward certification goals.
- Challenge: Evidence collection gaps emerge when monitoring isn’t configured properly initially.
Solution requires implementing automated logging early during preparation phases. Calendar reminders prompt manual evidence collection for controls lacking automation. Regular evidence reviews identify gaps while remediation remains possible.
- Challenge: Understanding audit report nuances confuses stakeholders unfamiliar with attestation standards.
The solution involves requesting auditor education sessions explaining the report structure and terminology. Reviewing sample reports before engagement sets appropriate expectations about content. Management can then communicate certification value effectively to customers and partners.
How Qualitas Consulting Can Help with SOC 2 in Qatar
Partnering with local experts transforms overwhelming compliance challenges into structured success.
Qualitas Consulting specializes in guiding Qatar businesses through SOC 2 implementation seamlessly. Our team understands regional challenges and international certification standards deeply. We don’t just identify gaps—we work alongside you to implement practical solutions.
Our comprehensive services include:
- Gap analysis and readiness assessments reveal your current compliance position
- Control design and implementation tailored to Qatar’s business environment
- Complete documentation support, including policies, procedures, and system descriptions
- Internal audit preparation through mock assessments, eliminating surprises
- Auditor liaison services, managing relationships, and coordinating evidence requests professionally
- Ongoing compliance support ensuring sustained certification through annual renewals
- Integration with ISO frameworks, leveraging existing management systems efficiently
We’re available 24/7 for urgent questions throughout your journey. Our proven track record across technology, financial services, and healthcare sectors demonstrates consistent results. Contact us today for a complimentary readiness assessment to discover your certification pathway.
Ready to Begin Your SOC 2 Compliance Journey With Confidence?
Qualitas Consulting brings proven expertise in ISO certification and compliance frameworks to Qatar businesses. Our team guides you through every checklist step, from initial gap analysis to final audit completion successfully.
Contact us today for a complimentary readiness assessment and discover how we accelerate your SOC 2 certification while maintaining operational efficiency. Let’s transform compliance complexity into your competitive advantage together.



